- 1 - ¿Para qué sirve?
- 2 - ¿Cómo tomar?
- 3 - ¿Qué contiene?
- 4 - Preguntas frecuentes
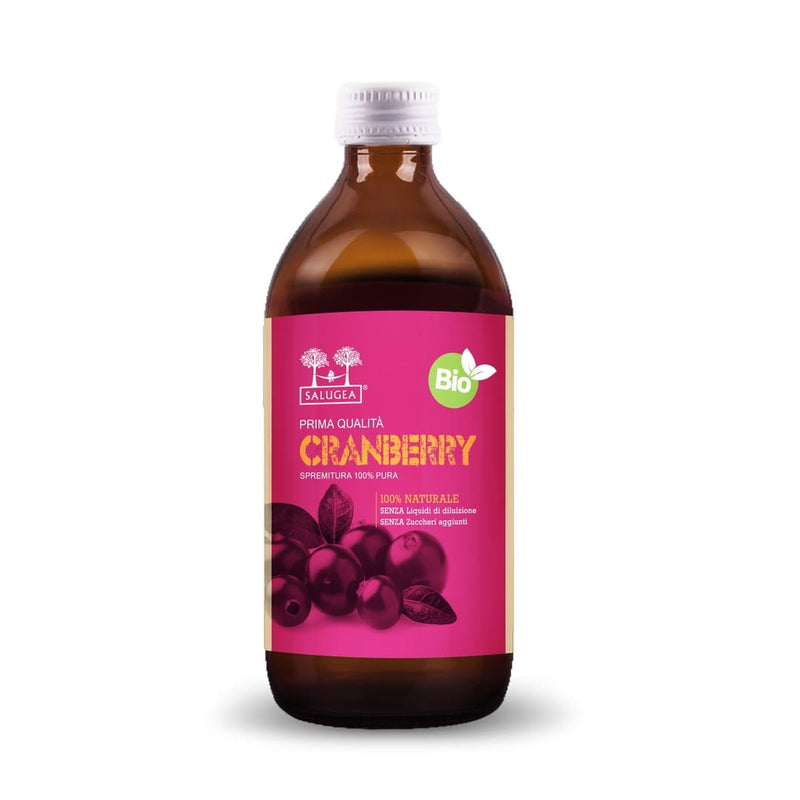
Zumo de Cramberry: Expimida 100% Pura
El Zumo de Cramberry Primera Calidad Salugea es útil por su acción de sostén a la funcionalidad de las vías urinarias (vejiga y uretra), y para el drenaje fisiológico de los fluidos corporales.
El Zumo de Cramberry Primera Calidad Salugea es un integrador alimentario obtenido exprimiendo en frío de las frutas nativas de Cranberry (Vaccinium macrocarpum Aiton), una planta nativa de las estepas pantanosas y humedales de América del Norte.
Il modo migliore per assumere il Succo di Cranberry Bio Salugea è a stomaco vuoto:
Puoi assumere dai 25 ml ai 50 ml al giorno. In particolare:
- 25 ml in fase preventiva e di sostegno.
- 50 ml in fase acuta (cioè quando ci sono fastidi conclamati alle vie urinarie) per 4-5 giorni.
Il momento migliore per assumere il Succo di Cranberry Bio è al mattino al risveglio. In questo caso ti consigliamo di aspettare 10’-15’ prima di fare colazione.
N.B. Tutti i Succhi Salugea sono BIOLOGICI. Questo significa che devi conservarli in frigorifero dopo l’apertura e consumarli nei tempi indicati sulla confezione.
N.B 2. Se il sapore risultasse intenso puoi diluire il prodotto in acqua o succo di frutta. Efficacia e risultati garantiti!
Durata del trattamento
Già dopo i primi giorni/settimane potrai constatare i risultati. Ti consigliamo di portare avanti il trattamento per 2 – 3 mesi per consolidare e mantenere nel tempo i benefici ottenuti.
Ogni volta che finisci un mese di trattamento ti suggeriamo di fare una pausa di 2-3 giorni prima di iniziare il flacone successivo.
Provalo con gli attivi di:
- Sanuril Formula Potenziata: per un’azione ancora più mirata sul benessere e sui fastidi alle vie urinarie ed evitare le recidive.
- Diuresan Formula Potenziata: per favorire la diuresi e allontanare velocemente i batteri dalle vie urinarie.
Avvertenze
La data di conservazione indicata si riferisce al prodotto integro, conservato in luogo fresco ed asciutto e lontano da sorgenti di luce e di calore. Una volta aperto conservare il flacone ben chiuso in frigorifero a + 4°C e consumare in circa 3 settimane. Tenere fuori dalla portata dei bambini sotto i tre anni. Non eccedere le dosi raccomandate per l'assunzione giornaliera. Gli integratori non vanno intesi come sostituti di una dieta variata ed equilibrata e di uno stile di vita sano.
Cranberry biologico (Vaccinium macrocarpum Aiton) succo del frutto 100% puro.
Valori Nutrizionali del Succo di Cranberry Bio Salugea
Tabella Nutrizionale (Valori Medi)
|
Per 100 ml |
Per dose 50 ml |
|
Calorie: 147 kJ - 35 kcal |
74 kJ - 18 kcal |
|
Grassi: 0,1 g |
0,05 g |
|
di cui Grassi Saturi: 0,1 g |
0,03 g |
|
Carboidrati: 6,2 g |
3,1 g |
|
di cui Zuccheri: 6,2 g |
3,1 g |
|
Proteine: 0,3 g |
0,15 g |
|
Sale: 0,05 g |
0,025 g |
Contiene naturalmente zuccheri (privo di zuccheri aggiunti)
L’apporto di sale è dovuto al sodio naturalmente presente nel prodotto
1 Howell A, Souza D, Roller M, Fromentin E. Comparison of the Anti-Adhesion Activity of Three Different Cranberry Extracts on Uropathogenic P-fimbriated Escherichia coli: a Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo Controlled, Ex Vivo, Acute Study. Nat Prod Commun. 2015;10(7):1215-1218.
2 Sihra N, Goodman A, Zakri R, Sahai A, Malde S. Nonantibiotic prevention and management of recurrent urinary tract infection. Nat Rev Urol. 2018;15(12):750-776. doi:10.1038/s41585-018-0106-x.
3 Bruyère F, Azzouzi AR, Lavigne JP, et al. A Multicenter, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study Evaluating the Efficacy of a Combination of Propolis and Cranberry (Vaccinium macrocarpon) (DUAB®) in Preventing Low Urinary Tract Infection Recurrence in Women Complaining of Recurrent Cystitis. Urol Int. 2019;103(1):41-48. doi:10.1159/000496695.
4 Shaheen G, Akram M, Jabeen F, et al. Therapeutic potential of medicinal plants for the management of urinary tract infection: A systematic review. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2019;46(7):613-624. doi:10.1111/1440-1681.13092.
5 Kim SH, Ha US, Lee HR, et al. Do Escherichia coli extract and cranberry exert preventive effects on chronic bacterial prostatitis? Pilot study using an animal model. J Infect Chemother. 2011;17(3):322-326. doi:10.1007/s10156-010-0170-5.
Nemzer BV, Al-Taher F, Yashin A, Revelsky I, Yashin Y. Cranberry: Chemical Composition, Antioxidant Activity and Impact on Human Health: Overview. Molecules. 2022;27(5):1503. Published 2022 Feb 23. doi:10.3390/molecules27051503.
Recurrent urinary tract infection and urinary Escherichia coli in women ingesting cranberry juice daily: a randomized controller trial. Stapleton AE, Dziura J, Hooton TM, Cox ME, Yarova-Yarovaya Y, Chen S, Gupta K. Mayo Clin Proc. 2012 Feb;87(2):143-50. doi: 10.1016/j.-mayocp.2011.10.006.
Evaluation of the effect of cranberry juice on symptoms associated with a urinary tract infection. Bass-Ware A, Weed D, Johnson T, Spurlock A. Urol Nurs. 2014 May-Jun;34(3):121-7.
Cranberry-containing products for prevention of urinary tract infections in susceptible populations: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Wang CH, Fang CC, Chen NC, Liu SS, Yu PH, Wu TY, Chen WT, Lee CC, Chen SC. Arch Intern Med. 2012 Jul 9;172(13):988-96. doi: 10.1001/archinternmed. 2012.3004. Review.
I nostri testi hanno scopo divulgativo, non vanno intesi come indicazione di diagnosi e cura di stati patologici e non vogliono sostituirsi in alcun modo al parere del Medico.
Cod. Min. Sal.: 136427
I nostri testi hanno scopo divulgativo, non vanno intesi come indicazione di diagnosi e cura di stati patologici e non vogliono sostituirsi in alcun modo al parere del Medico.
Zumo de Cramberry
Mirtillo Rosso Americano
Domande Frequenti sull'integratore
Altre Domande?
Se non hai trovato la risposta alla tua domanda, puoi contattarci: