- 1 - ¿Para qué sirve?
- 2 - ¿Cómo tomar?
- 3 - ¿Qué contiene?
- 4 - Preguntas frecuentes
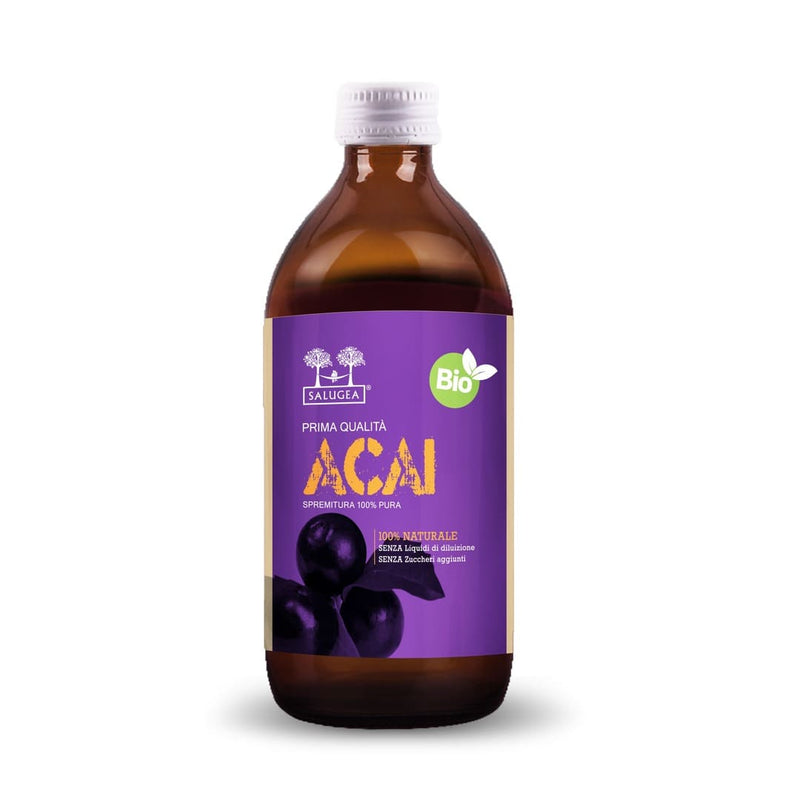
Zumo de Acai: Expimida 100% Pura
El Zumo de Acai Salugea sostiene la circulación protegiendo los vasos sanguíneos y el corazón. Desarrolla acción antioxidante y desintoxicante, favorece el control fisiológico de las grasas y azúcares en la sangre. El Zumo de Acai Primera Calidad Salugea es un integrador alimentario, obtenido con fruta exprimida en frío de frutas nativas de Acai (Euterpe oleracea Mart.) Originarias de la selva amazónica.
Il modo migliore per assumere il Succo di Acai Bio Salugea è a stomaco vuoto:
Puoi assumere dai 25 ml ai 50 ml al giorno. In particolare:
- 25 ml in fase preventiva e di sostegno.
- 50 ml in fase acuta e per qualche giorno.
Il momento migliore per assumere il Succo di Acai Bio è al mattino al risveglio. In questo caso ti consigliamo di aspettare 10’-15’ prima di fare colazione.
N.B. Tutti i Succhi Salugea sono biologici. Questo significa che devi conservarli in frigorifero dopo l’apertura e consumarli nei tempi indicati sulla confezione.
N.B 2. Se il sapore risultasse troppo intenso puoi diluire il prodotto in acqua o succo di frutta. Efficacia e risultati garantiti!
Durata del trattamento
Già dopo i primi giorni/settimane potrai constatare i risultati. Ti consigliamo di portare avanti il trattamento per 2 – 3 mesi per consolidare e mantenere nel tempo i benefici ottenuti.
Ogni volta che finisci un mese di trattamento ti suggeriamo di fare una pausa di 2-3 giorni prima di iniziare il flacone successivo.
Provalo con gli attivi di:
- Liposan Forte Nuova Formula: per l’equilibrio di colesterolo e trigliceridi nel sangue.
- Omega 3 Krill Oil: per l’apporto di Omega 3 da Krill di qualità superiore.
Avvertenze
La data di conservazione indicata si riferisce al prodotto integro, conservato in luogo fresco ed asciutto e lontano da sorgenti di luce e di calore. Una volta aperto conservare il flacone ben chiuso in frigorifero a + 4°C e consumare in circa 3 settimane. Tenere fuori dalla portata dei bambini sotto i tre anni. Non eccedere le dosi raccomandate per l'assunzione giornaliera. Gli integratori non vanno intesi come sostituti di una dieta variata ed equilibrata e di uno stile di vita sano.
Acai biologico (Euterpe oleracea Mart.) succo del frutto 100% puro.
Valori Nutrizionali del Succo di Acai Bio Salugea
Tabella Nutrizionale (Valori Medi)
|
Per 100 ml |
Per dose 50 ml |
|
Calorie: 210 kJ - 50 kcal |
105 kJ - 25 kcal |
|
Grassi: 0,2 g |
0,1 g |
|
di cui Grassi Saturi: 0,04 g |
0,02 g |
|
Carboidrati: 13 g |
6,5 g |
|
di cui Zuccheri: 13 g |
6,5 g |
|
Proteine: 0,4 g |
0,2 g |
|
Sale: 0,01 g |
0,005 g |
- Contiene naturalmente zuccheri (privo di zuccheri aggiunti)
- L’apporto di sale è dovuto al sodio naturalmente presente nel prodotto
1 Matta FV, Xiong J, Lila MA, Ward NI, Felipe-Sotelo M, Esposito D. Chemical Composition and Bioactive Properties of Commercial and Non-Commercial Purple and White Açaí Berries. Foods. 2020;9(10):1481. Published 2020 Oct 16. doi:10.3390/foods9101481.
2 Emma L. Wightman, David O. Kennedy, Chapter 70 - Polyphenol Modulation of Blood Flow and Oxygenation, Editor(s): Ronald Ross Watson, Victor R. Preedy, Sherma Zibadi, Polyphenols in Human Health and Disease, Academic Press, 2014, doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-398456-2.00070-0.
3 Mirele da Silveira Vasconcelos, Erika Freitas Mota, Neuza Felix Gomes-Rochette, Diana Célia Sousa Nunes-Pinheiro, Seyed Mohammad Nabavi, Dirce Fernandes de Melo, Chapter 3.1 - Açai or Brazilian Berry (Euterpe oleracea), Editor(s): Seyed Mohammad Nabavi, Ana Sanches Silva, Nonvitamin and Nonmineral Nutritional Supplements, Academic Press, 2019, doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-812491-8.00017-5.
4 Cartolano FC, Dias GD, Miyamoto S, Damasceno NRT. Omega-3 Fatty Acids Improve Functionality of High-Density Lipoprotein in Individuals With High Cardiovascular Risk: A Randomized, Parallel, Controlled and Double-Blind Clinical Trial. Front Nutr. 2022;8:767535. Published 2022 Feb 23. doi:10.3389/fnut.2021.767535.
5 Bazinet RP, Chu MW. Omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids: is a broad cholesterol-lowering health claim appropriate?. CMAJ. 2014;186(6):434-439. doi:10.1503/cmaj.130253.
6 Hussain T, Tan B, Yin Y, Blachier F, Tossou MC, Rahu N. Oxidative Stress and Inflammation: What Polyphenols Can Do for Us?. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016:7432797. doi:10.1155/2016/7432797.
7 Xie C, Kang J, Li Z, et al. The açaí flavonoid velutin is a potent anti-inflammatory agent: blockade of LPS-mediated TNF-α and IL-6 production through inhibiting NF-κB activation and MAPK pathway. J Nutr Biochem. 2012;23(9):1184-1191. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2011.06.013.
8 Flavonoids from acai (Euterpe oleracea Mart.) pulp and their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. Kang J, Xie C, Li Z, Nagarajan S, Schauss AG, Wu T, Wu X. Food Chem. 2011 Sep 1;128(1):152-7. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem. 2011.03.011.
9 Alqurashi RM, Galante LA, Rowland IR, Spencer JP, Commane DM. Consumption of a flavonoid-rich açai meal is associated with acute improvements in vascular function and a reduction in total oxidative status in healthy overweight men. Am J Clin Nutr. 2016;104(5):1227-1235. doi:10.3945/ajcn.115.128728.
10 Lavefve L , Howard LR , Carbonero F . Berry polyphenols metabolism and impact on human gut microbiota and health. Food Funct. 2020;11(1):45-65. doi:10.1039/c9fo01634a.
11 U.S. DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE - FOODDATA CENTRAL NATIVO ACAI - PURE ACAI BERRY PUREE
I nostri testi hanno scopo divulgativo, non vanno intesi come indicazione di diagnosi e cura di stati patologici e non vogliono sostituirsi in alcun modo al parere del Medico.
Cod. Min. Sal.: 136423
I nostri testi hanno scopo divulgativo, non vanno intesi come indicazione di diagnosi e cura di stati patologici e non vogliono sostituirsi in alcun modo al parere del Medico.
Zumo de Acai
Acai: integratore liquido 100% puro
Domande Frequenti sull'integratore
Altre Domande?
Se non hai trovato la risposta alla tua domanda, puoi contattarci: